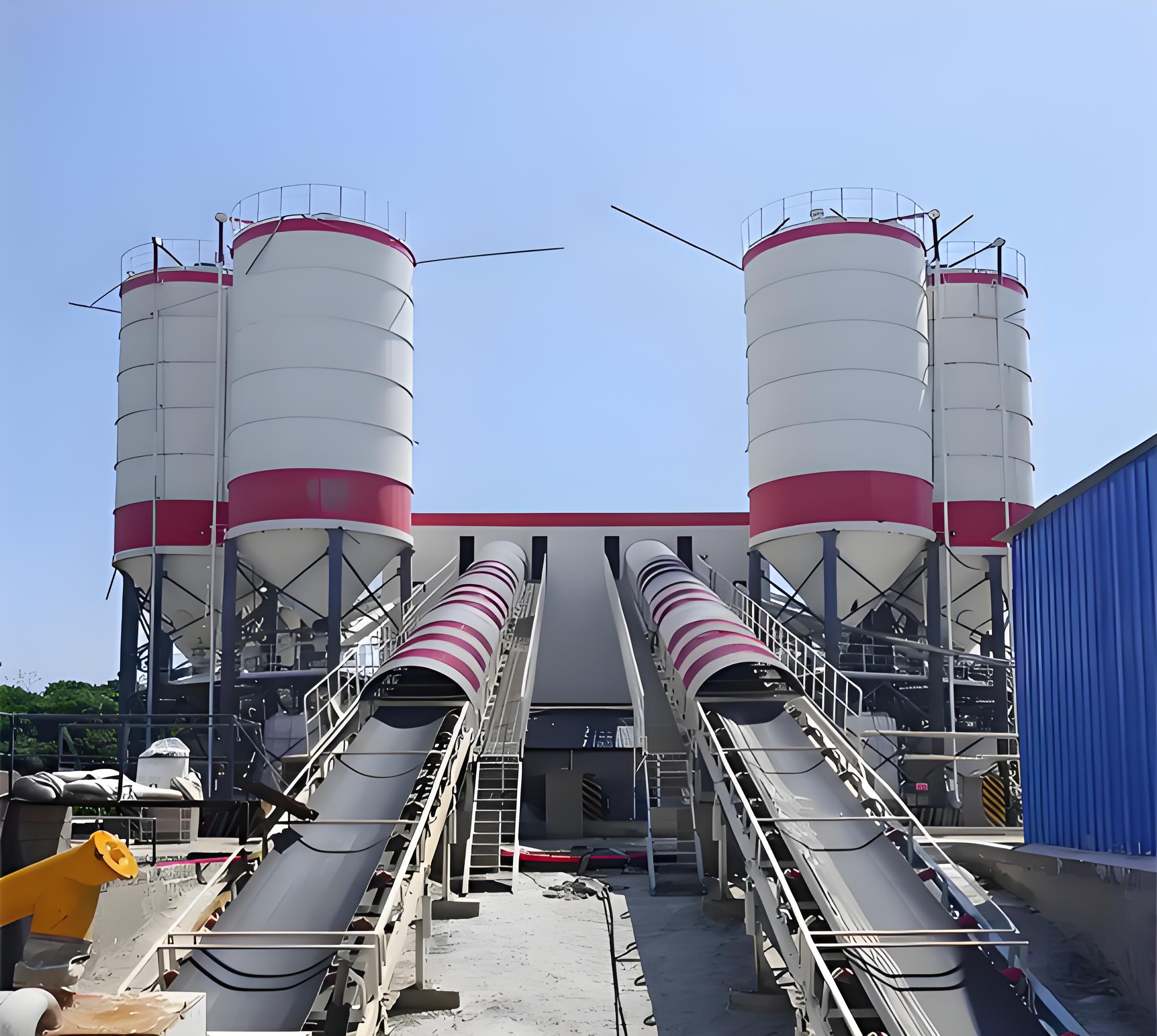
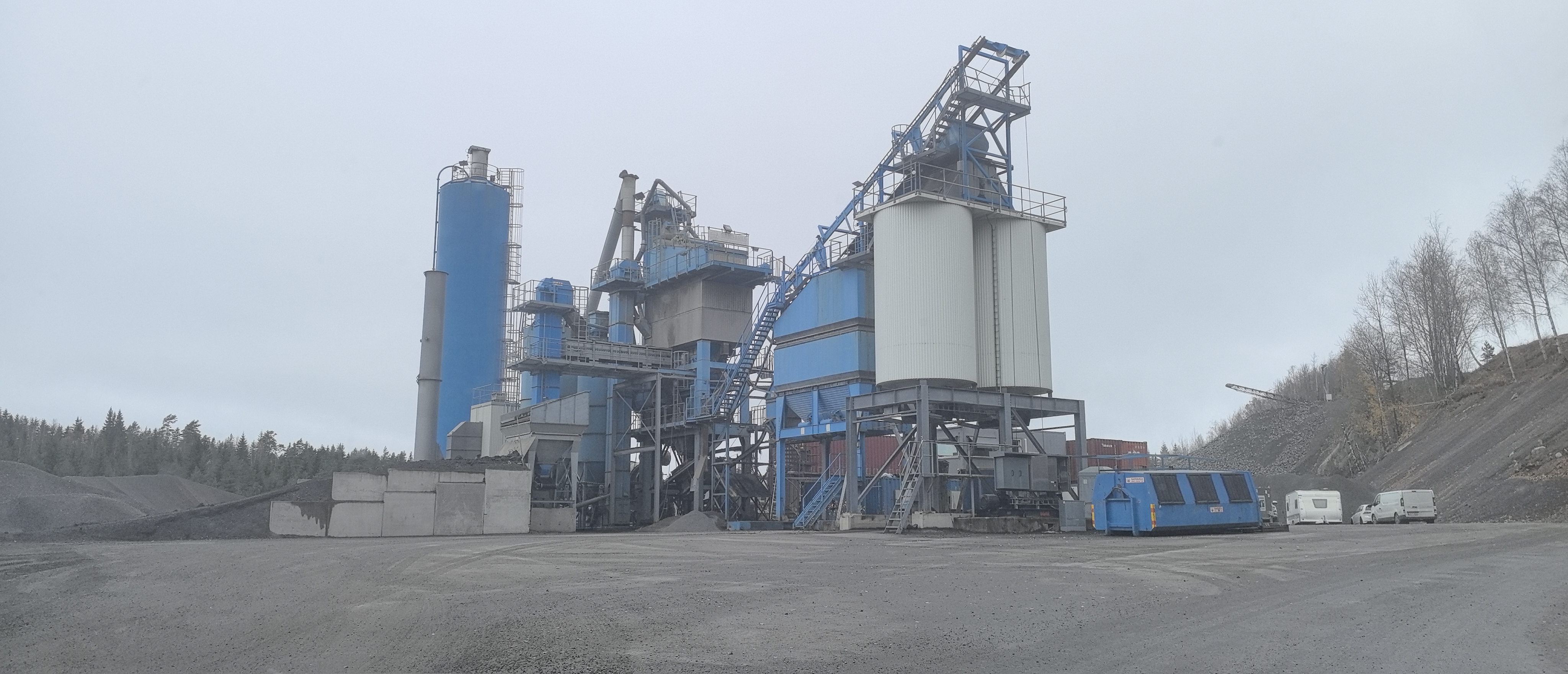
Concrete batching plants are essential for modern construction, providing ready mix concrete efficiently for projects ranging from residential complexes to major infrastructure. However, these plants can generate significant environmental impacts, including dust, noise, wastewater, and energy consumption.
Managing these issues effectively is not only regulatory compliance but also cost-saving and brand-enhancing. In fact, one mobile concrete batching plant near Jakarta reduced dust emissions by 40% simply through proper material storage and dust collection systems.
This guide explores the environmental challenges of concrete batching plants, offering practical solutions and strategies for operators, engineers, and project managers.
Definition & Importance
Environmental issues in concrete batching plants refer to the negative impacts on air, water, soil, and noise levels caused by concrete production processes. These include:
-
Dust emissions from aggregate handling and cement silos.
-
Wastewater from mixer and truck washing.
-
Noise from mixers, conveyors, and vehicles.
-
Energy consumption from electrical motors and pumps.
Addressing these issues is critical. Plants that implement environmental management systems not only comply with local regulations but also enhance community relations and reduce fines. Interestingly, environmental improvements often coincide with operational efficiency, reducing waste and improving concrete quality.
Components / Structure / Key Parts
Each part of a concrete batching plant can contribute to environmental impacts if not properly managed:
Aggregate Bins & Conveyors
Dust escapes during unloading and conveying. Installing covered conveyors and regular bin cleaning prevents airborne particulate matter.
Cement Silos & Weighing Systems
Cement dust is highly polluting. Proper silo sealing, dust collectors, and accurate weighing reduce both waste and airborne emissions.
Mixers
Mixers generate noise and residual wastewater. Soundproof enclosures and efficient discharge systems minimize impacts.
Washout & Water Systems
Truck and mixer washing can contaminate soil and water. Implementing closed-loop water recycling systems helps reduce pollution.
Control Panels & Electrical Systems
Energy consumption is indirect environmental impact. Optimized automation and energy-efficient motors reduce electricity usage and carbon footprint.
Case Insight: In a concrete batching plant in the Philippines, covering aggregate bins and installing a central dust collector reduced PM10 emissions by over 50%, improving air quality for nearby residential areas.
How It Works / Step-by-step Guide
Step 1: Environmental Assessment
-
Conduct a baseline environmental assessment.
-
Identify dust, noise, water discharge points, and energy hotspots.
-
Use monitoring equipment like PM sensors, sound meters, and water quality testers.
Step 2: Dust Control Measures
-
Install baghouse filters on cement silos.
-
Use misting systems for aggregate piles.
-
Seal transfer points on conveyors to limit fugitive dust.
-
Ensure mobile concrete batching plants have portable dust suppression systems.
Step 3: Noise Reduction
-
Enclose mixers and pumps in soundproof cabins.
-
Use low-noise conveyors and reduce vehicle idling time.
-
Maintain equipment to avoid excessive vibration and mechanical noise.
Step 4: Wastewater Management
-
Capture washout water in sedimentation tanks.
-
Treat water for reuse in mixing or site dust suppression.
-
Monitor pH and suspended solids to meet local environmental standards.
Step 5: Energy Efficiency
-
Replace old motors with energy-efficient drives.
-
Optimize batching sequences to minimize idle running.
-
Use predictive maintenance to prevent energy waste from inefficient operation.
Practical Example: A ready mix concrete plant in India installed a closed-loop water recycling system and baghouse filters, achieving compliance with local environmental standards while cutting water usage by 60%.
Benefits / Competitive Advantages
Managing environmental issues effectively provides multiple business advantages:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Avoid fines and shutdowns.
-
Cost Savings: Reduce waste of cement, aggregates, and water.
-
Community Relations: Lower dust and noise complaints improve brand reputation.
-
Operational Efficiency: Cleaner equipment and better air quality improve worker productivity.
Notably, some advanced plants combine environmental controls with automated batching software. For example, sensors can detect cement spillage and trigger alarms or corrective actions, minimizing waste and emissions simultaneously.
Cost & Setup / ROI Analysis
Implementing environmental solutions requires initial investment, but the long-term ROI is substantial:
-
Dust collectors: $10,000–$50,000 depending on plant size.
-
Water recycling system: $15,000–$60,000.
-
Noise enclosures and insulation: $5,000–$20,000.
-
Energy-efficient motors and automation upgrades: $10,000–$30,000.
ROI Considerations:
-
Reduced material loss saves thousands per month.
-
Lower water usage cuts utility costs.
-
Compliance avoids fines and project delays.
-
Positive community perception may increase project wins.
Maintenance & Common Issues
Dust Control Maintenance:
Water System Maintenance:
Noise Control Maintenance:
Monitoring:
-
Use environmental sensors to track PM, NOx, pH, and noise levels continuously.
-
Maintain logs for regulatory audits and continuous improvement.
Issue Handling:
-
Clogged dust collectors: clean or replace filters immediately.
-
Water contamination: activate treatment cycles or replace sediment tanks.
-
Noise complaints: review operational schedules and implement additional soundproofing.
How to Choose the Right Type
Selecting a plant type affects environmental management:
-
Stationary Concrete Batching Plant: Easier to install permanent environmental controls like full dust collection and water recycling systems.
-
Mobile Concrete Batching Plant: Requires compact, portable solutions for dust and water control.
-
Mini/Compact Plants: May combine dust suppression, water recycling, and low-noise mixers into a single modular system.
Pro Tip: Evaluate local regulations before purchase. Some countries require dust collectors, water treatment, or noise mitigation as mandatory components of plant installation.
FAQs
What are the main environmental issues of concrete batching plants?
Dust, wastewater, noise, energy consumption, and material waste are primary concerns.
How can I reduce dust emissions effectively?
Install baghouse filters, cover aggregate piles, seal transfer points, and use misting or vacuum systems.
Is wastewater treatment necessary?
Yes, capturing and recycling washout water prevents soil and water pollution while saving costs.
Can automation help with environmental management?
Absolutely. Modern software can monitor emissions, detect spillages, and control batching to minimize waste and energy usage.