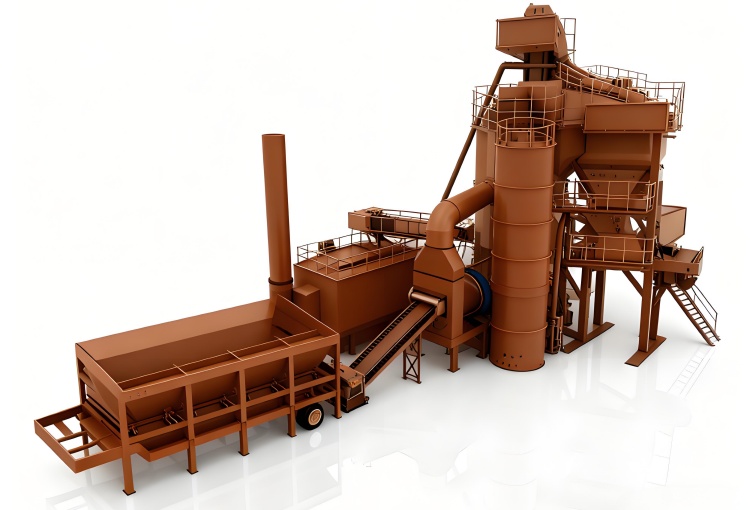
In global infrastructure development, asphalt mixing plants are the beating heart of road construction. They determine not only the quality of asphalt pavement but also the speed, cost, and sustainability of projects. Whether it’s a batch asphalt mixing plant, mobile asphalt mixing plant, or continuous asphalt mixing plant, understanding how these systems work and how to optimize them is key to maximizing your investment.
1. The Core Function and Importance of Asphalt Mixing Plants
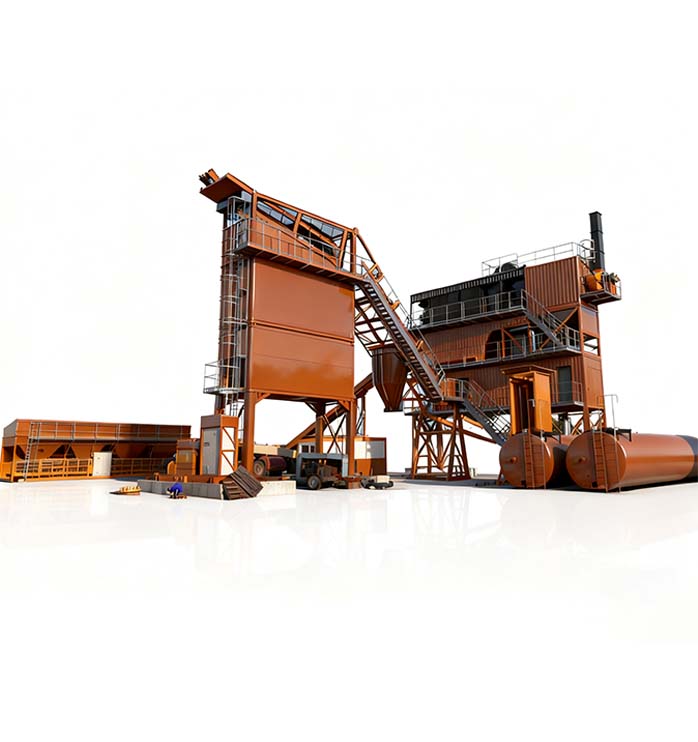
An asphalt mixing plant is an integrated system that produces asphalt concrete by combining aggregates, sand, filler, and bitumen in precise proportions. The result is a durable road surface that can withstand heavy loads, extreme weather, and long-term wear.
In fact, without properly calibrated and efficient asphalt mixing plants, infrastructure projects face inconsistent quality, high energy waste, and costly delays.
1.1 The Global Demand
According to market reports, global demand for asphalt mix plants is projected to grow steadily at 4–5% CAGR through 2030, driven by highway modernization in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. China, India, and Indonesia remain the top markets for asphalt batch mix plant suppliers.
2. How an Asphalt Mixing Plant Works: The Complete Process
To understand performance optimization, it’s essential to review the asphalt batching plant process.
2.1 Material Feeding and Drying
Cold aggregates are fed into the drying drum via conveyors. In a batch asphalt mixing plant, the drying drum removes moisture using a high-efficiency burner.
Notably, optimizing burner temperature can reduce fuel use by up to 12%, improving ROI.
2.2 Screening and Weighing
After drying, aggregates are screened into different sizes. The system weighs them precisely according to the asphalt recipe—this is where plant calibration plays a major role.
2.3 Mixing and Storage
The aggregates are then transferred into the mixer, combined with bitumen and filler. In modern asphalt batch plants, the entire cycle can complete in 45 seconds, producing up to 400 tons per hour.
2.4 Automation Control Systems
Advanced asphalt batch plant control software enables real-time adjustment of temperature, bitumen ratio, and mixing time—ensuring consistent quality and compliance with international standards.
3. Types of Asphalt Mixing Plants: Choosing the Right Model
Different projects require different plant configurations. Let’s analyze the three most common types.
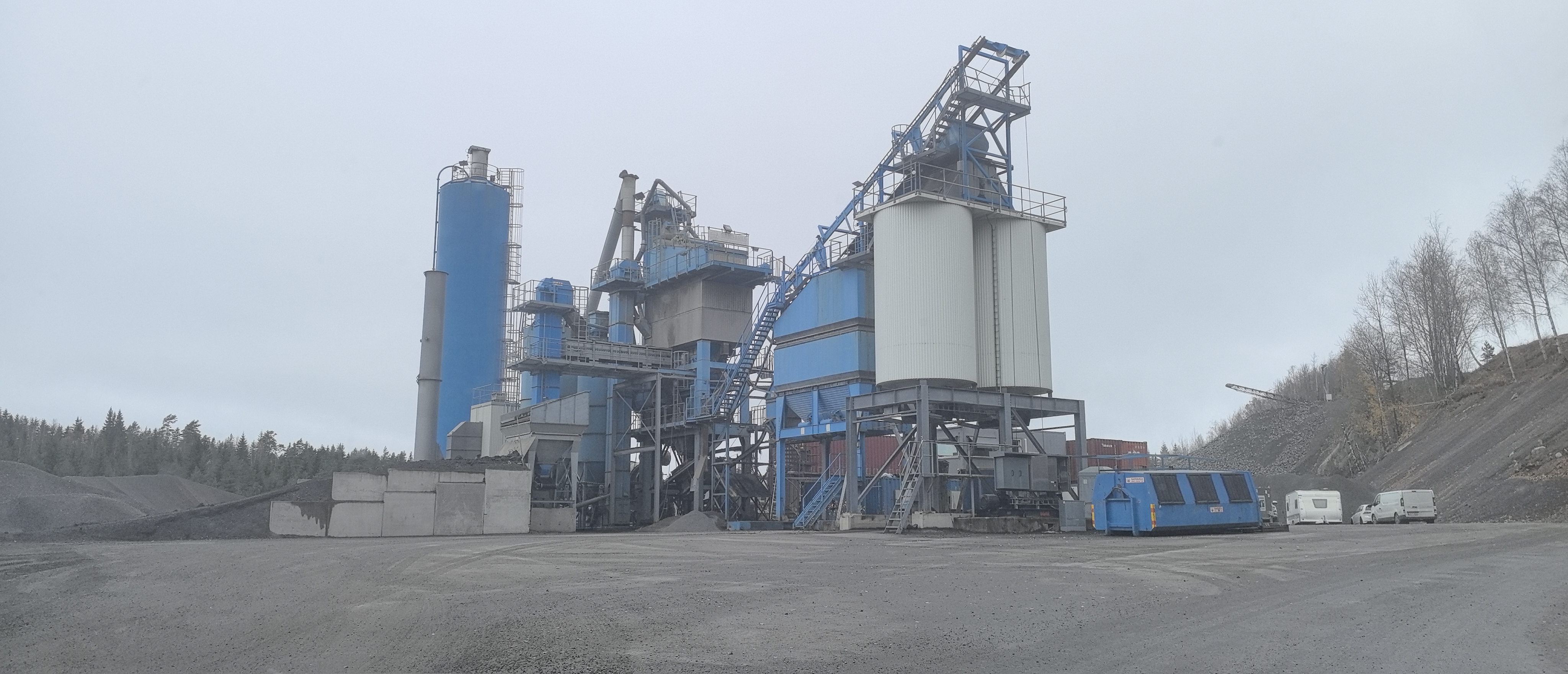
3.1 Batch Asphalt Mixing Plant
This type produces asphalt in batches, offering precise control over material composition. It’s ideal for projects where different mix designs are needed.
Batch plants are widely used by asphalt batch mix plant exporters in Europe and Asia.
3.2 Continuous Asphalt Mixing Plant
Unlike batching systems, continuous plants operate non-stop, suitable for high-volume projects. They have fewer moving parts, reducing maintenance downtime.
Interestingly, the continuous asphalt mixing plant is preferred in developing regions where fast road deployment is essential.
3.3 Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant
Mobility is key for contractors working on remote sites. A mobile asphalt mixing plant can be installed in 3–5 days and relocated easily.
This model reduces transportation costs and improves construction flexibility—crucial for rural or island projects.
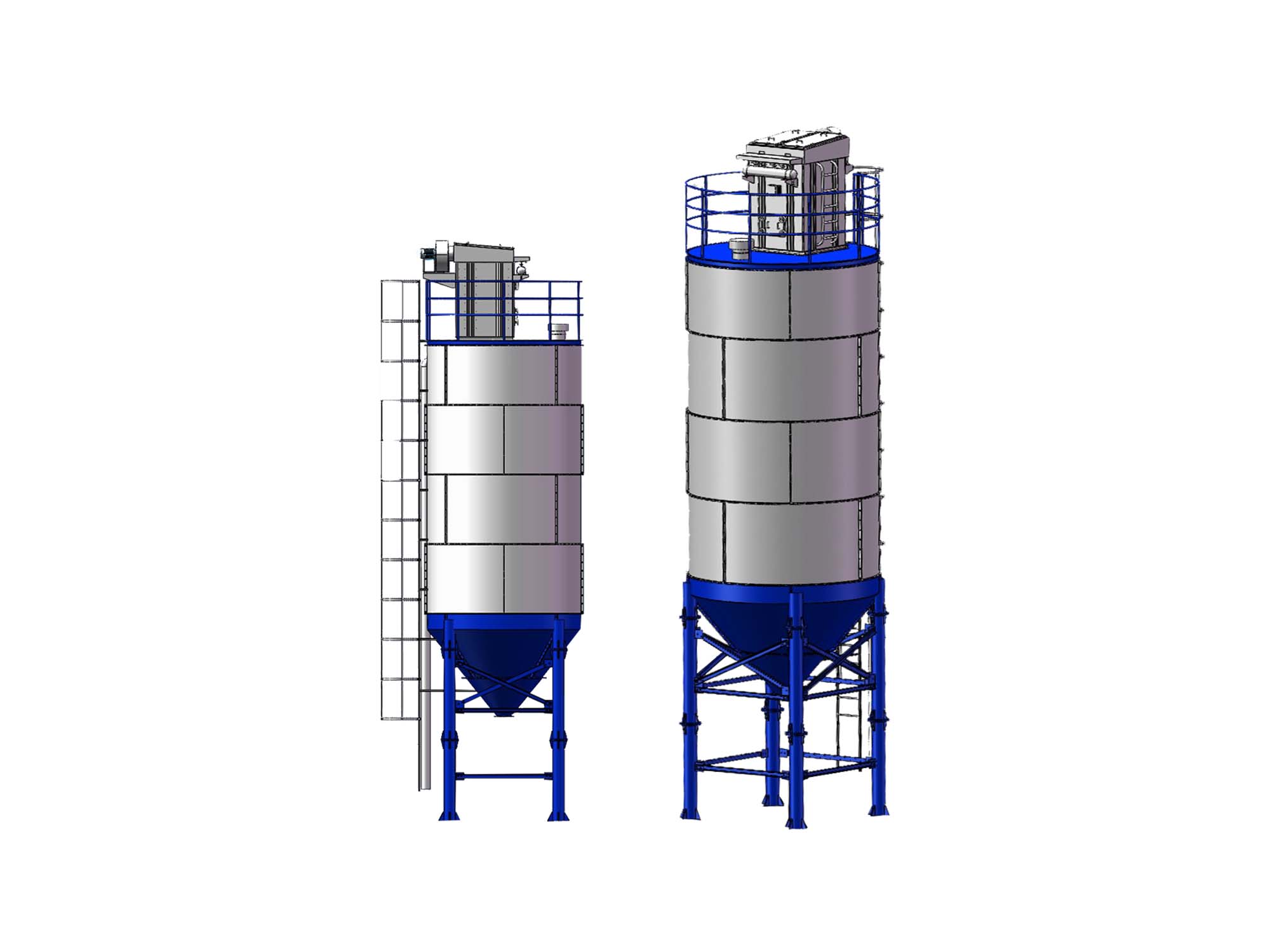
4. Key Components and Their Roles
Each asphalt concrete mixing plant comprises several core components, each affecting efficiency and quality.
-
Cold Aggregate Feeder: Ensures steady material flow.
-
Drying Drum: Evaporates moisture for consistent asphalt quality.
-
Bag Filter System: Controls dust emissions to meet global environmental standards.
-
Bitumen Tank: Maintains precise temperature for optimal viscosity.
-
Control Cabin: The brain of the operation—manages batching, heating, and mixing parameters.
If any of these elements are underperforming, production costs and output quality suffer. Regular inspection and preventive maintenance can extend service life by 20% or more.
5. Cost and ROI: Understanding Asphalt Mixing Plant Economics
When investing in an asphalt mixing plant, price and long-term ROI are critical. Let’s break down the main cost drivers.
5.1 Initial Investment
-
Stationary asphalt mixing plant: $180,000–$450,000
-
Mobile asphalt mixing plant: $120,000–$300,000
-
Continuous asphalt mixing plant: $150,000–$350,000
5.2 Operating Costs
Operating costs include fuel, power, maintenance, and labor. Energy accounts for 35–45% of total operating costs.
5.3 ROI Calculation
With smart automation and proper calibration, contractors can achieve ROI within 18–24 months. A TTM asphalt mixing plant or Bukaka asphalt plant equipped with a heat recovery system can save up to $20,000 annually in fuel.
6. Technological Innovations in Modern Asphalt Plants
The evolution of asphalt technology has been dramatic. Today’s systems are smarter, cleaner, and more efficient.
6.1 IoT and Automation
IoT sensors monitor aggregate temperature, fuel use, and emissions. Data analytics identify inefficiencies and recommend real-time adjustments.
A hot asphalt mixing plant integrated with digital control can improve mixing accuracy by 7–10%.
6.2 Energy Optimization
Modern burners achieve over 95% combustion efficiency. Heat recycling reduces gas consumption by 15%.
6.3 Dust and Emission Control
To meet tightening environmental laws, plants use baghouse filters that capture 99% of dust.
This aligns with the latest KBLI asphalt mixing plant classification for green compliance in Southeast Asia.
7. Operational Challenges and How to Solve Them
Despite technical advancements, operators face recurring challenges.
7.1 Inconsistent Asphalt Temperature
This often results from poor burner calibration or moisture in aggregates.
Solution: Regularly check the asphalt mixing plant layout and ensure uniform aggregate drying.
7.2 Bitumen Leakage
Caused by aging pipes or improper sealing.
Solution: Use high-quality seals rated for 200°C and inspect weekly.
7.3 Dust Emissions
Improper filter maintenance can exceed legal dust limits.
Solution: Replace filter bags every 2,000 hours and monitor with an online system.
8. Enhancing ROI Through Optimization and Maintenance
To maximize ROI from your asphalt plant investment, focus on three pillars: performance, cost, and sustainability.
8.1 Performance Optimization
-
Calibrate scales monthly.
-
Clean mixing paddles daily.
-
Monitor aggregate moisture in real time.
8.2 Cost Efficiency
-
Use reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) up to 40%.
-
Install frequency converters to reduce energy peaks.
-
Schedule preventive maintenance to avoid unplanned downtime.
8.3 Sustainability Initiatives
Adopting warm mix asphalt reduces CO₂ emissions by 30%.
Installing solar-assisted power for control systems further reduces operational costs.
9. How to Choose the Right Supplier
Partnering with reliable asphalt mixing plant manufacturers ensures quality and after-sales support.
When evaluating asphalt batch mix plant suppliers, consider:
In China, many leading asphalt mixing plant manufacturers such as SDCAD, Zoomlion, and XCMG have integrated digital monitoring and modular design for global clients.
10. Future Trends: Toward Greener, Smarter Asphalt Production
As global climate policies tighten, the industry is shifting toward low-emission asphalt plants.
By 2030, 60% of new asphalt batch plants will include energy recovery and AI-based process optimization.
Interestingly, modular systems are emerging as the next big thing—enabling fast relocation, plug-and-play setup, and minimal foundation requirements.
11. Conclusion: Building the Future with Smart Asphalt Mixing Plants
The asphalt mixing plant is more than a machine—it’s a strategic investment in efficiency, quality, and sustainability.
Contractors who embrace automation, smart calibration, and preventive maintenance achieve faster ROI and stronger competitive advantage.
In fact, the road to success is paved not just with asphalt—but with the right technology behind it.